-
- Actuators
- Coil Design
- Electromagnetic Brakes & Clutches
- Inductors
- Levitators
- MRI
- Motors
- Alternators and Generators
- Electromagnetic Brakes and Clutches
- Sensors
- Loudspeakers
- Magnetic Encoding
- Relays and Contactors
- Solenoids
- Shielding
- Electromagnets
- Magnetic Bearings
- Magnetic Signatures
- Magnetic Fixtures
- Magnets
- Non Destructive Testing
- Particles
-
- Antenna Radiation Characteristics
- Simulation of an Airplane
- EM Simulation of a Desktop
- EM Compatability and EM Interference
- Cable Junctions and Terminations
- Filters
- Lightning Strikes
- Microwave Circuits
- Microwave Ovens
- MRI
- Near Field Analysis
- Radar Cross Sections
- Radio Frequency Cavities
- Reflector Antennas
- Sensors
- Ultra Wideband Antennas
- Waveguides
- Antennas
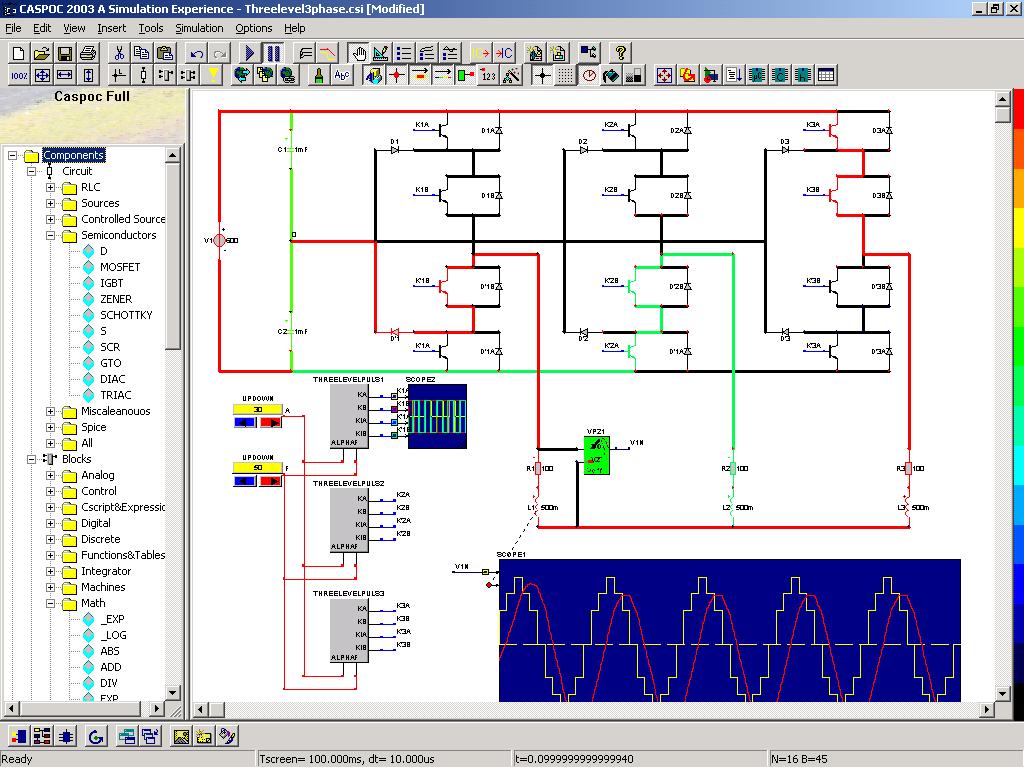
High Precision Servo Drives
The accuracy of servo drives depends on all components in the drive train. Every non-linearity or drift in encoders, quantization of current and voltage measurements, delay in control algorithms and even the back-lash in gear boxes have to be included in the simulation model. The multiphysics library in CASPOC™ includes special models from which the entire servo drive can be built.
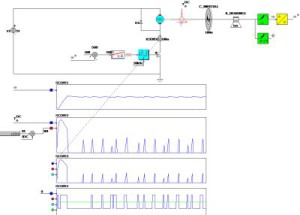
Highly detailed electric machine and single phase actuator models (including all position and saturation as well as efficiency data) are calculated in FEM and imported into CASPOC™ for a complete drive simulation.
By using the generic electrical machine and generic control blocks, a drive train concept is easily set up. From a concept to a ready-for-production prototype, detailed electrical machines can be modeled from FEM, including all delay and non-linearity in each and every component.